Edge CDN Media Networks
Current methods for media delivery and consumption are fast being replaced by multi-path gateways to deliver content. The lines between wireless,satellite and layered networks are blurred as now, much of media is delivered to and consumed by mobile subscribers. Content distribution occurs through network backbone vendors such as Akamai, LeveL3, CDNetworks, or carriers such as Verizon, AT&T and Comcast, and other cable providers.
Content providers such as Netflix, Disney, Amazon, Alibaba, Hulu and many others operate on a mix of proxy servers and one or more fibre backbones.To improve quality of service, their goal is to minimize paths to any endpoint (mobile device, USB devices like Roku and Chromecast, set top box, even game consoles. This has spawned new approaches to CDNs. In simple terms, copies of media are located at different nodes of the selected pathways, delivered from devices which are located geographically close to the user, improving access time and buffering of content
Ad hoc networks, some using mesh topology with IPV4/IPV6 endpoint addressing, are able to deliver content and much reduced transmission cost. With the ongoing battle for Net Neutrality, streaming content owners are exploring new ways to avoid paying a higher price for delivery.
Ad hoc wireless networking usually refers to client devices connecting directly to each other in any convenient topology, without using an access point. In a networking context, ad hoc implies a network topology spontaneously created or updated as nodes connect. Device-to-device ad hoc networking is an ideal approach to connect vehicles. As transport vehicles move, an everchanging mesh network allows them to join or disconnect with other vehicles.
With static edge networks, like set top devices, a CDN can intelligently distribute one or more copies of media to the edge and then control how this media is passed to other connected devices without requiring transmission from a central data content source. Companies such as Quilt employ an edge CDN cloud that configures routing using Software Defined Network architecture that uses both IP and logical routing which changes routes based on load demand and content frequency.
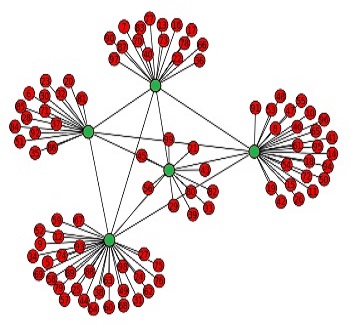
| CDN with supernodes |
 |
| CDN with mesh nodes |
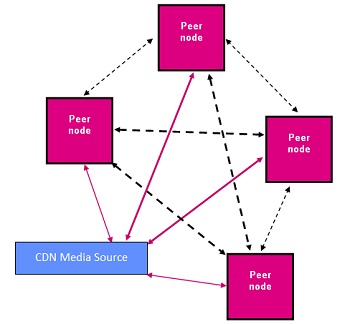 |
"In peer-to-peer (P2P) content-delivery networks, clients provide resources as well as use them. This means that unlike client-server systems, the content centric networks can actually perform better as more users begin to access the content (especially with protocols such as Bittorrent that require users to share). This property is one of the major advantages of using P2P networks because it makes the setup and running costs very small for the original content distributor." - Wikipedia
InterVault - Secure E2E transmission of media in motion
InterVault is a key component in the Ubivault Secure Edge CDN Module, a platform to securely connect one or nodes in an adhoc distributed media network. It is scalable, lightweight, certificate-free and supports:
- P2P E2E encryption
- Transcends firewalls, NAT
- Connects to Jigsaw fractal data
- Ideal for remote access to rich media eg. CAT, MRI
- Deployed in US military and government agencies
- Full range of collaborative tools:
- Stream & video share
- Stream & blockchain transaction monitoring
- Chat, VoIP, video conference